

OP AMP OFFSET VOLTAGE CALCULATION PLUS
But, the input at the negative terminal will give us an inverted amplified output.įrom the above discussion don’t get confused about the thing that plus voltage means V 1 is positive and minus means V 2 is negative as it is not so. The input at the positive terminal will get amplified at the output in the same way it is.

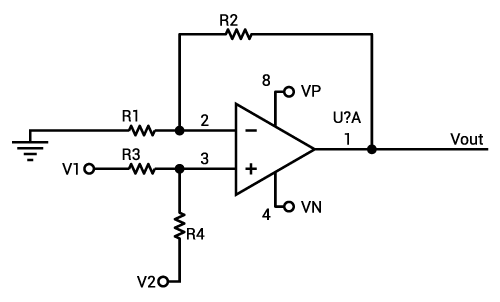
So, we will have a differential value at the inputĪnd at the output, we have an amplified output with gainĪs we have already discussed that positive indicates the non-inverting terminal and negative indicates the inverting terminal. V 2 is the input at inverting terminal of the Op-amp. V 1 is the input at non-inverting terminal and The diagram shown below shows the schematic symbol of an Op-amp. An Op-amp IC 741 has become an industry standard. The figure below shows the pin diagram of an Op-amp-įairchild in 1965 introduced the 1 st generation 709 and in 1968, still popular 2 nd generation 741 Op-amps introduced. When IC technology arrived, it became possible to place the Op-amp into a single 8 lead package. Op-amp was firstly built with a vacuum tube but in the early 1960s, transistors replaced vacuum tubes. So, we can say the amplifier is a differential amplifier that provides an amplified version of the differential input signal. The output of an op-amp is a difference value of the two inputs applied. Op-amps provides extremely high voltage gain, typically of order 200,000. Op-amps were basically designed to perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, differentiation, integration etc.īut, today op-amp provides a variety of other uses such as phase shifting, scale changing, sign changing, in oscillator circuits, pulse generators, comparator, converters etc.Īn op-amp act as a versatile device and can perform countless tasks when manufactured with integrated transistors, diodes, resistor and capacitor. It can be used to amplify ac as well as dc input signals. The two input terminal has one inverting input with a negative sign and one non-inverting input with a positive sign.Īs op-amps have high input impedance and low output impedance moreover has the ability to amplify signals of the frequency range from 0 Hz to 1 MHz. Following is an example connection of the ADC convertor that you can refer to when you design your circuit.This 3 terminal device consists of two high impedance input ports alongwith an output port.
You can choose the generic 8-bit ADC device from the Proteus library => Modelling Primitives => ADC_8 for this task. The output voltage signal from the analogue circuit should then be converted into an 8-bit digital signal, which represents the levels of the motor speed. Part 2: Design an 8-bit counter and a 4-to-7 decoder for the Seven-Segment display

Design the current amplification circuit using appropriate op-amp circuits so that you can achieve the required output voltage (2 to 3 V). Use an AC current source with a very low frequency of 0.01 Hz to emulate the slowly changed current output signal from the remote motor speed sensor. Part 1: Design a current amplification and filtering circuit The 8-bit signal should go through two 4-to-7 decoders so that the value of the 8-bit digital signal is displayed as two hexadecimal values on two seven-segment display devices to indicate the safe running speed of the motor in range 0-255 (i.e. After the conversion, a low pass filter is used to suppress any noise AC signals with frequency higher than 50 Hz.Īn 8-bit analogue-to-digital converter will be given and should be used to convert the output of the above analogue circuit into an 8-bit digital signal. Design a circuit to convert this signal into a voltage signal in the range from 2 to 3 V.
OP AMP OFFSET VOLTAGE CALCULATION FULL
Click to expand.ok full detail of project is as followsĪ remote motor speed sensor provides a current signal in the range of -2.5 to 2.5 mA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
